Dismate PE is a powerful system used to combat food moths present in food processing, manufacturing and distribution facilities. The pheromone-based technology works as a mating disruption system that has been used successfully in the food industry for over ten years.
Dismate PE is a preventative and curative treatment for food moth infestations in facilities such as cereal manufacturing facilities, chocolate factories, large scale commercial bakeries, nut or dried grain storage and grain silos.
Mating disruption technology is recommended for professional use to combat: Indian meal moth, Plodia interpunctella – Mill moth, Ephestia kuehniella – Warehouse moth/ Cocoa moth, Ephestia elutella – Tropical warehouse moth, Cadra cautella – Raisin moth, Cadra figulilella
Key Advantages
- Proven food moth control system with a 15 year track record
- Curative and preventative replacement to Methyl Bromide without downtime
- Is non-toxic and leaves zero residues in treated areas and commodities
- Continual preventative control strategy.
Requirements
- Continuous monitoring of moth population
- Application of pheromone traps for monitoring
- Maintain a good level of hygiene in food storage areas
- Evaluation of monitoring by hygiene and food safety officers.
The Pests
Plodia/Ephestia stored food moths are one of the most widespread and economically damaging pests of stored food commodities. The pests are a serious threat to the dried food processing industry as the larvae feed on and contaminate dry fruit, cereals, chocolate, nuts, legumes and other commodities causing serious financial losses and possible damage to brand integrity and reputation with the customer.
The Solution
Dismate PE offers Plodia/Ephestia control in a non-toxic, residue free way that results in no down-time for the facility, saving you time and money. The long-life sachets are active for up to 3 months and come in four colours to enable easy servicing for the pest controller. The sachets are metal detectable to provide additional safety measures.
Dismate PE works by disturbing the communication between male and female through:
- Masking the pheromone trail left by the female.
- Exhaustion of males through sparking premature excitation in their search for females.
- Confused males can then be found stationary and hovering around high pheromone release dispensers.
Integrated Pest Management
For optimal results with Dismate PE, there is a required need for performing continuous monitoring of moth population using Xlure RTU food moth pheromone traps.
Further precautions such as maintaining a clean and hygienic environment in food storage areas and monitoring by hygiene and food safety officers will help in the prevention of infestations in conjunction with Dismate PE.

Food Safety
- Dismate is a solid dispenser which is designed to be fixed to a surface away from food processing areas. Therefore, there is no likelihood of contact between the pheromone and the product.
- Dismate is made of durable plastic that is fixed to the wall with a nylon connector. It can only be removed by substantial effort or deliberate force to remove it.
- The pheromone used is nature identical to those produced by the insect itself, only in a much larger quantity. Dismate PE is considered to be non-toxic to humans and only released in negligible amounts.
- Dismate is arguably one of the safest and most cost-effective solutions available for the management of stored food moth pests.

Trial Results
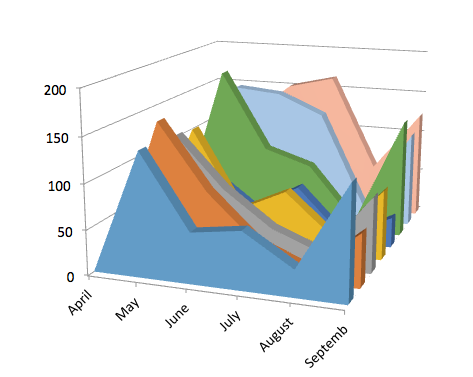
In one Dismate trial, the mating disruption system began controlling the moth population, but it began to peak back up after a time, see the graph. Further investigations showed that a consistent application of Dismate is required as well as thorough hygiene protocols, as residual populations of moths can remain in food debris under machinery etc.
It is clear that different facilities respond differently to Dismate due to the different food sources, storage times and hygiene practices playing an integral role in managing or introducing infestations.
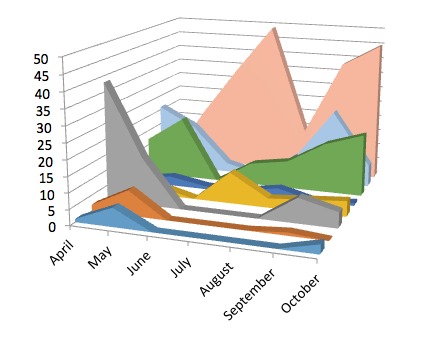
In the graph to the left, you can clearly see that some locations in the facility resulted in a complete reduction in moth populations, whilst other areas found very little control. Again this was the result of undesirable hygiene levels in those facilities, harbouring residual larval and pupal populations.